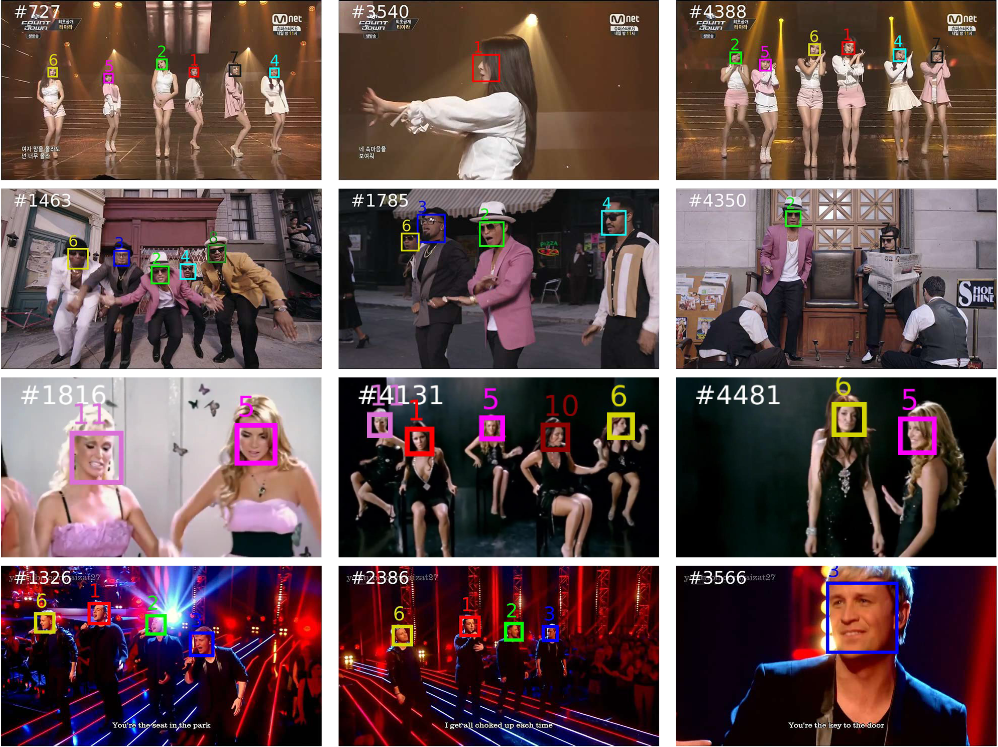
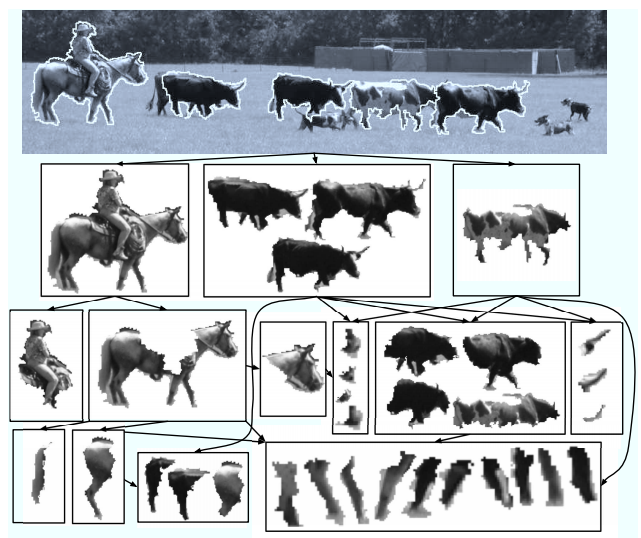
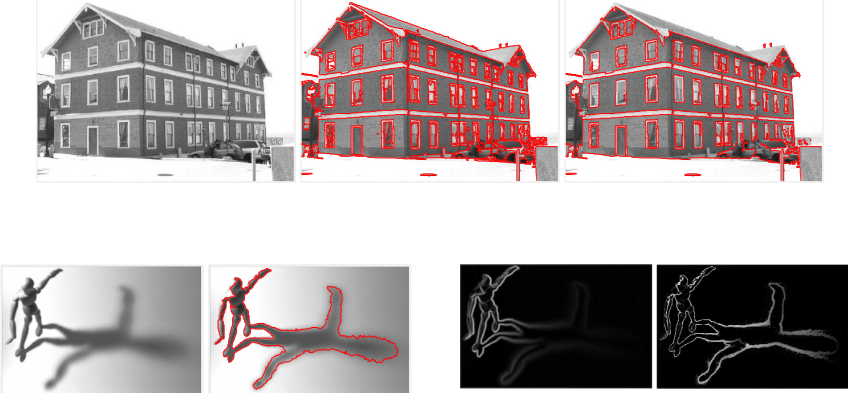
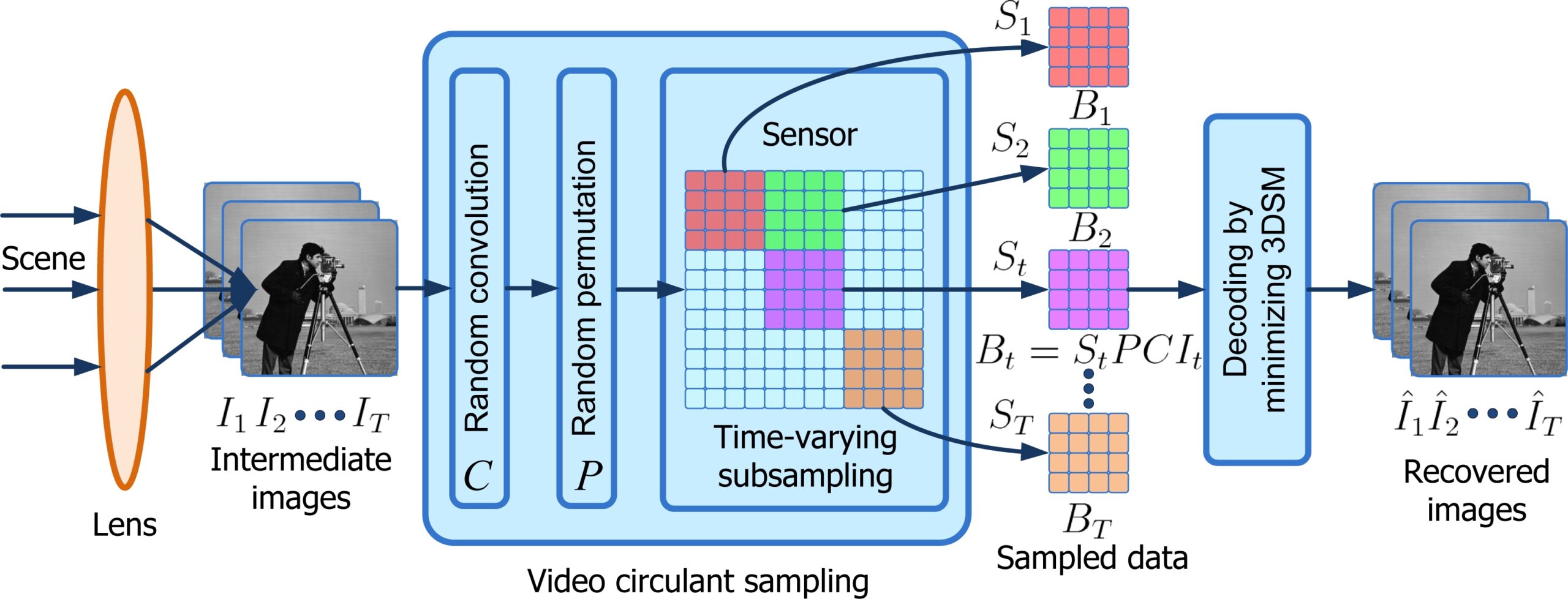
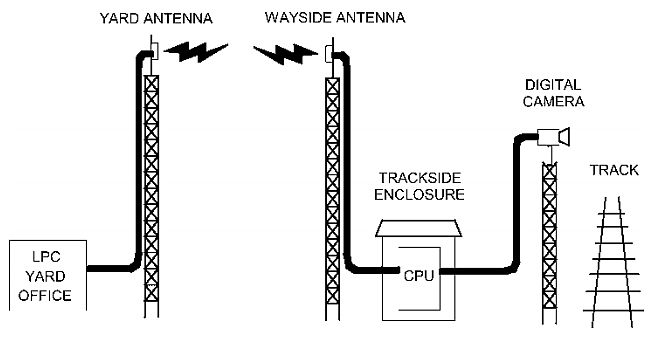
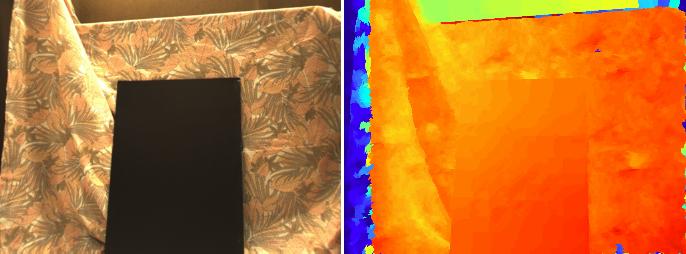
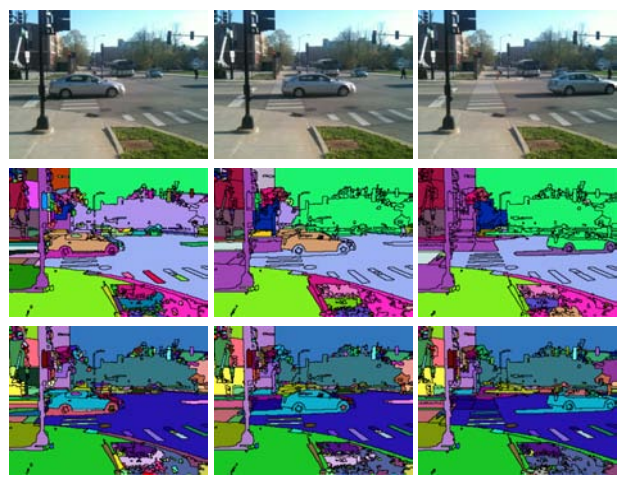
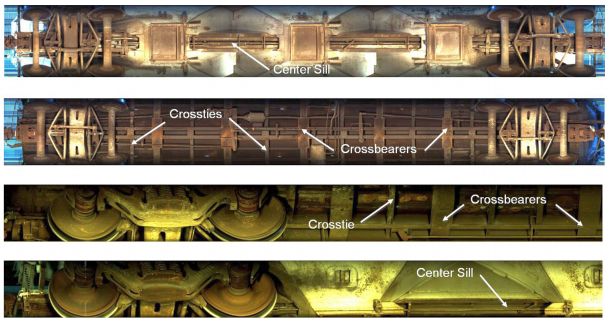
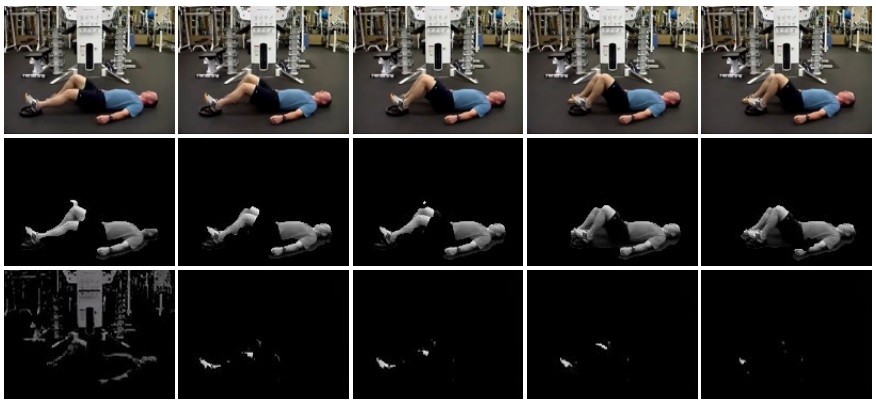
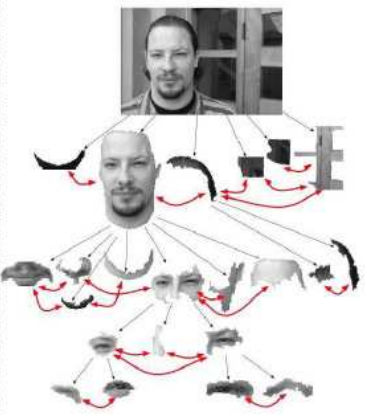
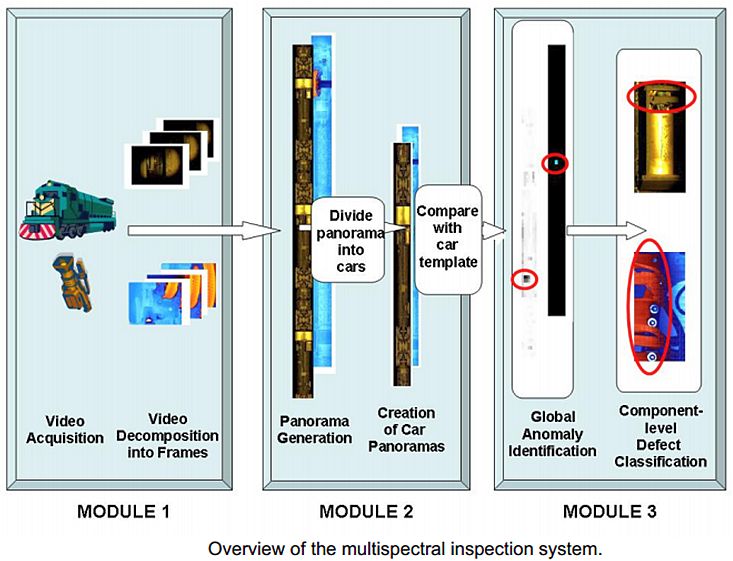
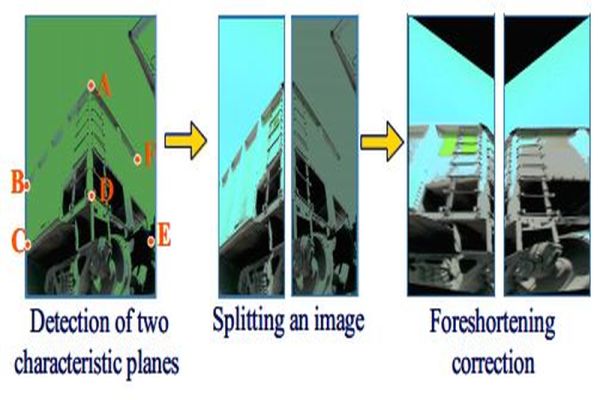
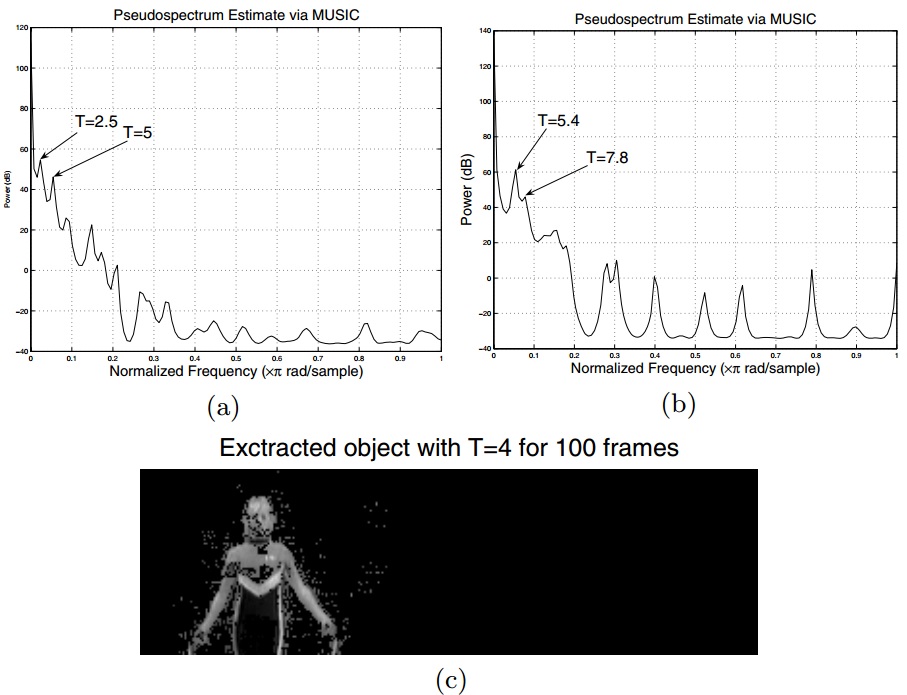
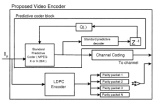
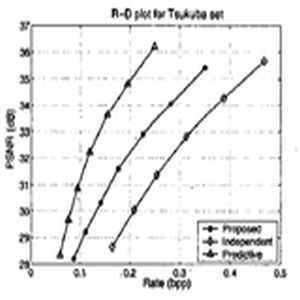
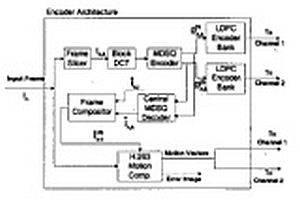
Multi-face tracking in unconstrained videos is a challenging problem as faces of one person often appear drastically
different in multiple shots due to significant variations in scale, pose, expression, illumination, and make-up. Existing multi-target tracking methods often use low-level features which are not sufficiently discriminative for identifying faces with such large appearance variations.